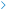There are two ways to add a Stories.
1. Quick Add
2. Add with more details
Quick Add
Quick Add helps and allows you to add a story quickly as it will ask for only basic information required for creating a new story. Once you have added story with quick add you can later edit the story if you want to give more details like story priority, business value, description, etc.
Add with more details
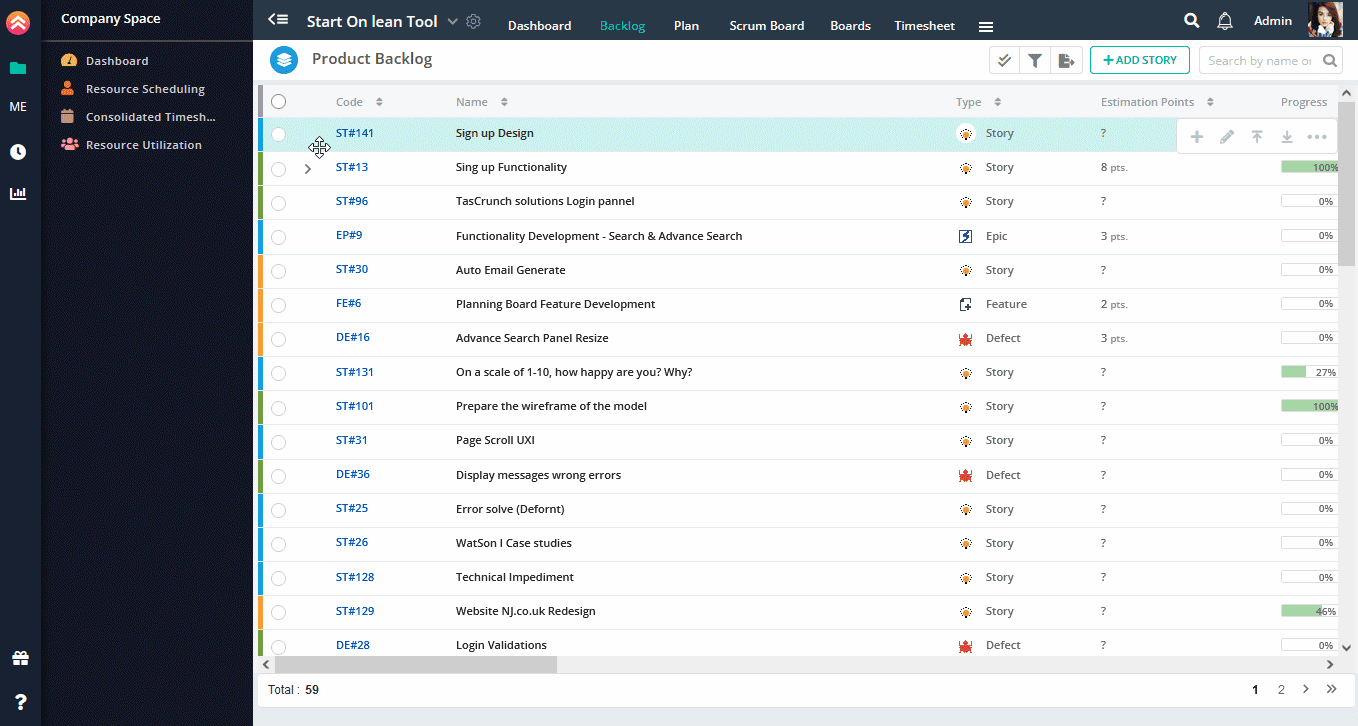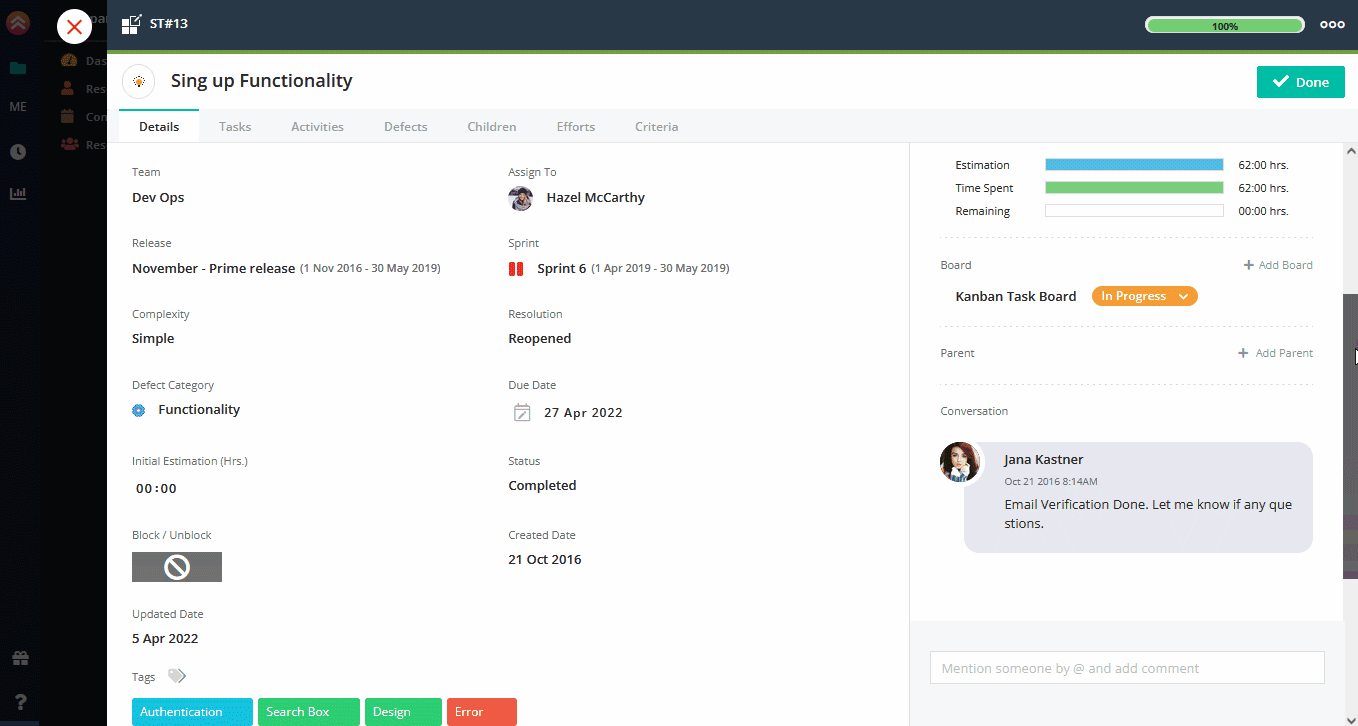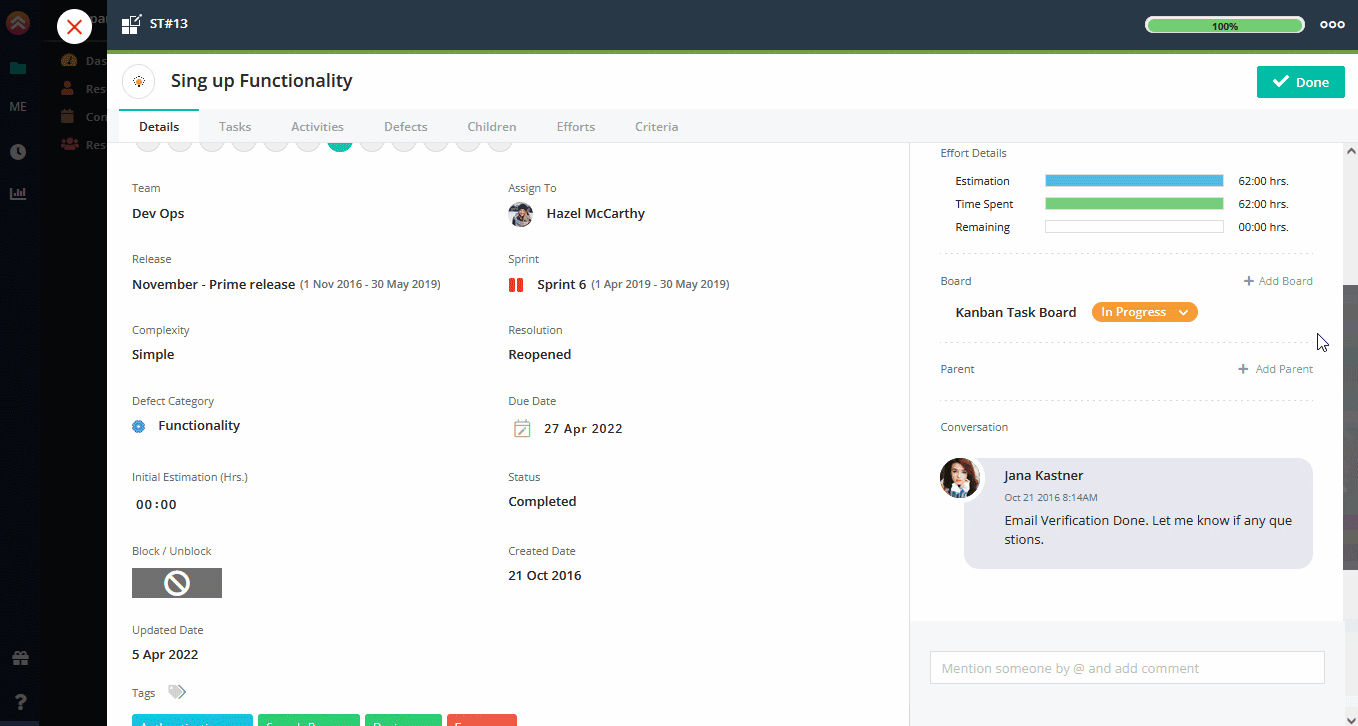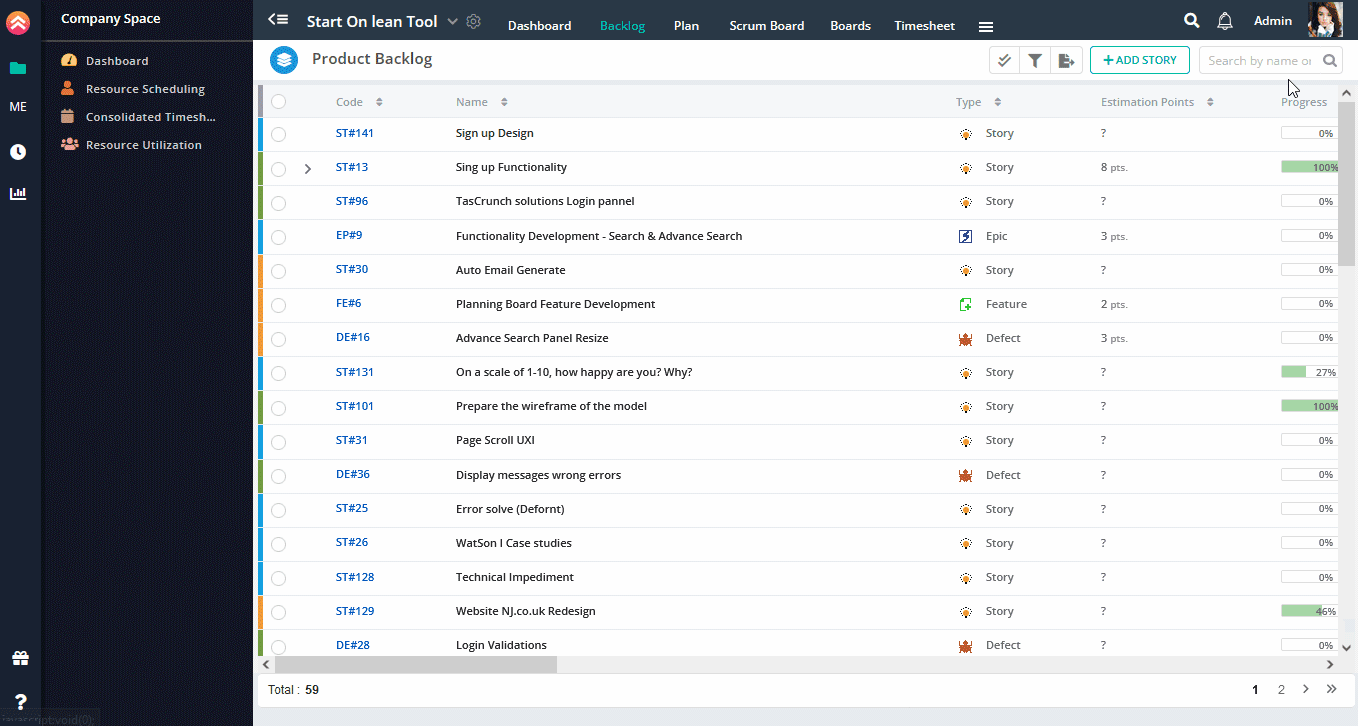
You can add stories with detail information. To add stories with detail,
1. Click on Story link on quick add view.
2. On click, full view will appear.
3. Fill more fields in Story Details.
You can fill all the details one by one.
Fields
Name:
The user story name will help you to refer a story easily. You can give relevant name to the story, for ex. if you have to develop search functionality you can give name to user story as Search Development.
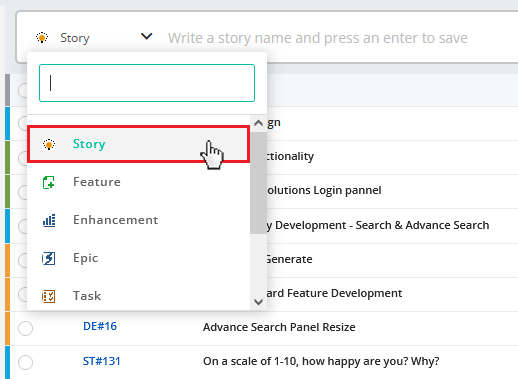
User story type:
You can select the story type from the drop down. There are six types of stories by default. All of them are symbolized with different icons. You can select the type under which your story falls.
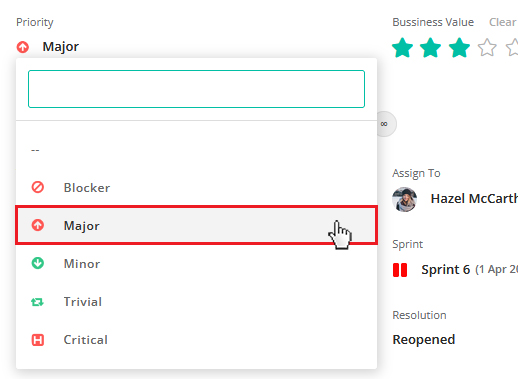
Priority:
You can set priority of the story as per the various aspects like importance of the story, when to deliver, business value, product vision, etc. Generally product owner defines the priority of a story keeping product vision in mind.
For e.g. If XYZ feature is less relevant but in future without that feature it is not possible to deliver product, product owner can select the priority type as Major or Must.
System will give you the option of selecting few priority type by default as shown below. If you want you can define priority type in “Story and Task Configuration” section.
Estimation Point:
Estimation Points or Story Points are used by scrum teams that measures the required effort in order to implement the story. From estimation points one can decide the complexity of the story or whether the story is more time consuming. The higher the estimation points are the more complex that story is to be considered. Generally Epics or the Parent stories are highly estimated, as those stories are big and complex. Quickscrum uses Fibonacci method for estimating a story.
Fibonacci series follows the pattern as “? 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40, 100 and ∞” Learn more about story estimation.
Importance of estimating a story:
Business Value field reveals the overall value of the story which will consider how cost-effective the story is. It should include the factors like customer need, business need, speed of ROI, development effort and cost.
Quickscrum presents business value in Fibonacci series, where it follows the pattern as ?, 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40, 100 and ∞.
The higher the business value is the more beneficial the story is considered. Learn more about Business value.
Description:
You can write the brief description of a user story in the description field that will explain user story in a better way and will help all team members to understand intention of the story clearly.
Acceptance Criteria:
Acceptance Criteria are the set of criteria which aims to successfully accomplish the story’s purpose. All the criteria must match with the functionality that has been developed, to verify the work done correctly or not. You can write down the acceptance criteria of user story in Acceptance Criteria field.
Release:
Select the release you want user story to be in.
Sprint:
Select the sprint you want user story to be in.
Team:
Assign the team to user story.
Assign To:
Assign a resource as owner to user story.
Status:
Select the status of user story. For e.g. If a story is ready for sprint and completely groomed you can select the status as Ready For Sprint.